Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or managing the condition for years, understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for maintaining a healthy and active life. This article explores the key treatments for diabetes, focusing on insulin, metformin, and other therapeutic options to help you make informed decisions for your health.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the pancreas, resulting in little or no insulin production. This type of diabetes typically manifests early in life and requires lifelong insulin therapy. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond to insulin properly. This form is more common and often linked to lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and genetics. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to severe complications such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney failure, vision problems, and even amputations. Therefore, managing blood sugar levels through proper treatment is essential to prevent these complications and improve the quality of life. In some cases, individuals with Type 2 diabetes may consider medications such as Mounjaro, which has shown promise in helping manage blood sugar levels.
Insulin Therapy: The Foundation of Diabetes Management
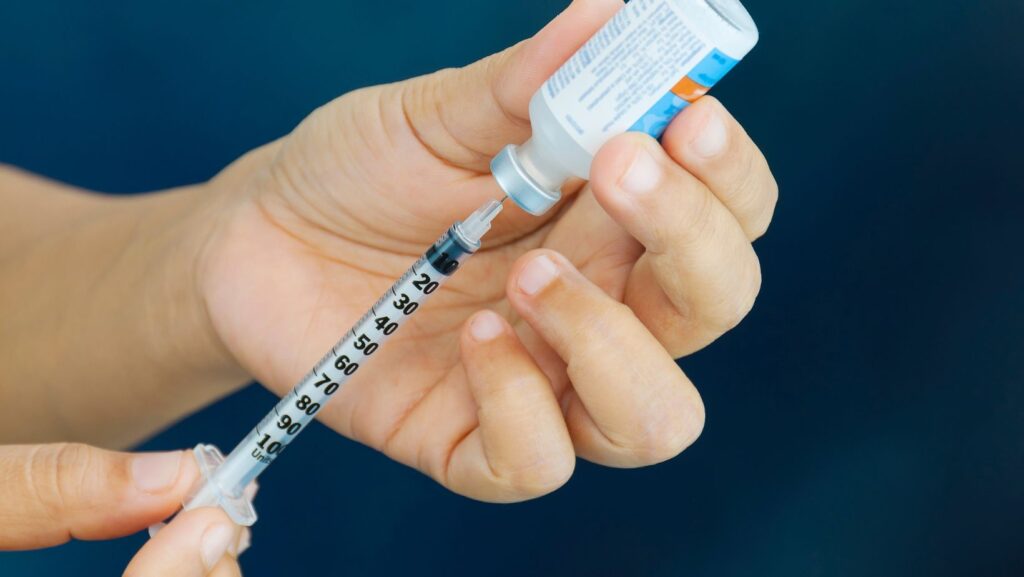
Insulin is one of the most common and crucial treatments for diabetes, especially for those with Type 1 diabetes. It is a hormone naturally produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy. In Type 1 diabetes, where insulin production is insufficient or absent, insulin therapy is necessary to manage blood sugar levels.

There are various types of insulin, each with different action times. Rapid-acting insulins begin to work within minutes, providing quick relief for high blood sugar. Long-acting insulins, on the other hand, provide a steady, baseline level of insulin over a prolonged period, typically 24 hours. Intermediate-acting insulins combine both short-term and long-term effects, while pre-mixed insulins offer a blend of rapid and long-acting insulin for convenient dosing.
Administering insulin can be done in several ways. The most common method is through injections, where patients use syringes or insulin pens to inject the hormone into subcutaneous tissue. Insulin pumps are also an option for those who prefer a more automated approach, delivering continuous insulin doses throughout the day. Additionally, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) help track blood sugar levels in real-time, providing valuable information for better insulin dose adjustments.
Metformin: The First Line of Defense for Type 2 Diabetes
Metformin is typically the first medication prescribed for individuals diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. Unlike insulin, which helps lower blood sugar directly, metformin works by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin and decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver. This helps reduce the overall blood sugar levels in the body.
Metformin is an oral medication, making it an easy choice for many patients who are looking for a non-injectable solution. It is generally well-tolerated and has a long history of use. One of the key benefits of metformin is that it does not cause weight gain, which is an advantage for many Type 2 diabetes patients who may already be managing excess weight. In fact, some studies suggest that metformin may even help with modest weight loss, making it an appealing choice for those looking to improve their overall health.
Other Oral Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
In addition to metformin, several other oral medications are available to help manage Type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways to help control blood sugar levels. Sulfonylureas are one of the most commonly prescribed classes of oral medications. These drugs help stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. While effective, they carry a risk of causing low blood sugar, especially if meals are skipped or if the medication dosage is too high.
DPP-4 inhibitors, such as sitagliptin, work by blocking an enzyme that breaks down incretins, hormones that stimulate insulin release and reduce glucagon levels. By increasing incretin activity, these drugs help lower blood sugar after meals. SGLT-2 inhibitors, like canagliflozin, are a newer class of drugs that help lower blood sugar by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the blood. This results in glucose being excreted in the urine. These medications have the added benefit of helping with weight loss and may reduce the risk of heart disease.
Injectable Medications Beyond Insulin
While insulin remains the cornerstone of diabetes management for many, several injectable medications have also been developed to help manage Type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 agonists, such as liraglutide and semaglutide, mimic the action of a naturally occurring hormone that promotes insulin secretion in response to meals and reduces the amount of glucose released by the liver. These medications not only help manage blood sugar but also contribute to weight loss, which is particularly beneficial for overweight patients.
Amylin analogs, like pramlintide, are used in combination with insulin therapy. These drugs help regulate blood sugar by slowing gastric emptying, reducing appetite, and preventing blood sugar spikes after meals.
Conclusion
Diabetes management is a multifaceted process that involves more than just medication. Understanding the various treatment options—insulin, metformin, oral medications, and injectable therapies—is key to making informed decisions about your health. Combined with healthy lifestyle changes, these treatments can help you live a full, active life while managing your diabetes effectively. With the right tools and support, it’s possible to keep blood sugar levels in check and reduce the risk of long-term complications.